Describe the Basic Steps That Are Used in Molecular Cloning
Cloning using somatic cell nuclear transfer 1. Cloning happens often in naturefor example when a cell replicates itself asexually without any genetic alteration or recombination.

17 1c Molecular And Cellular Cloning Biology Libretexts
The restriction enzymes cut the DNA at specific target sequences.

. In standard molecular cloning experiments the cloning of any DNA fragment essentially involves seven steps. Researchers have cloned a wide range of biological materials including genes cells. The first step of the general molecular cloning procedure is to obtain the desired insert which can be derived from DNA or mRNA from any cell type.
However the use of a common initial stepcalled either nuclear transplantation or somatic cell nuclear transfer. The basic process of cloning is the isolation of a DNA sequence from any species and insertion into a piece of carrier DNA called a vector for propagation inside a host species which is usually. Whenever compatible restriction enzyme sites are available on both insert and vector DNA sequences cloning is straightforward.
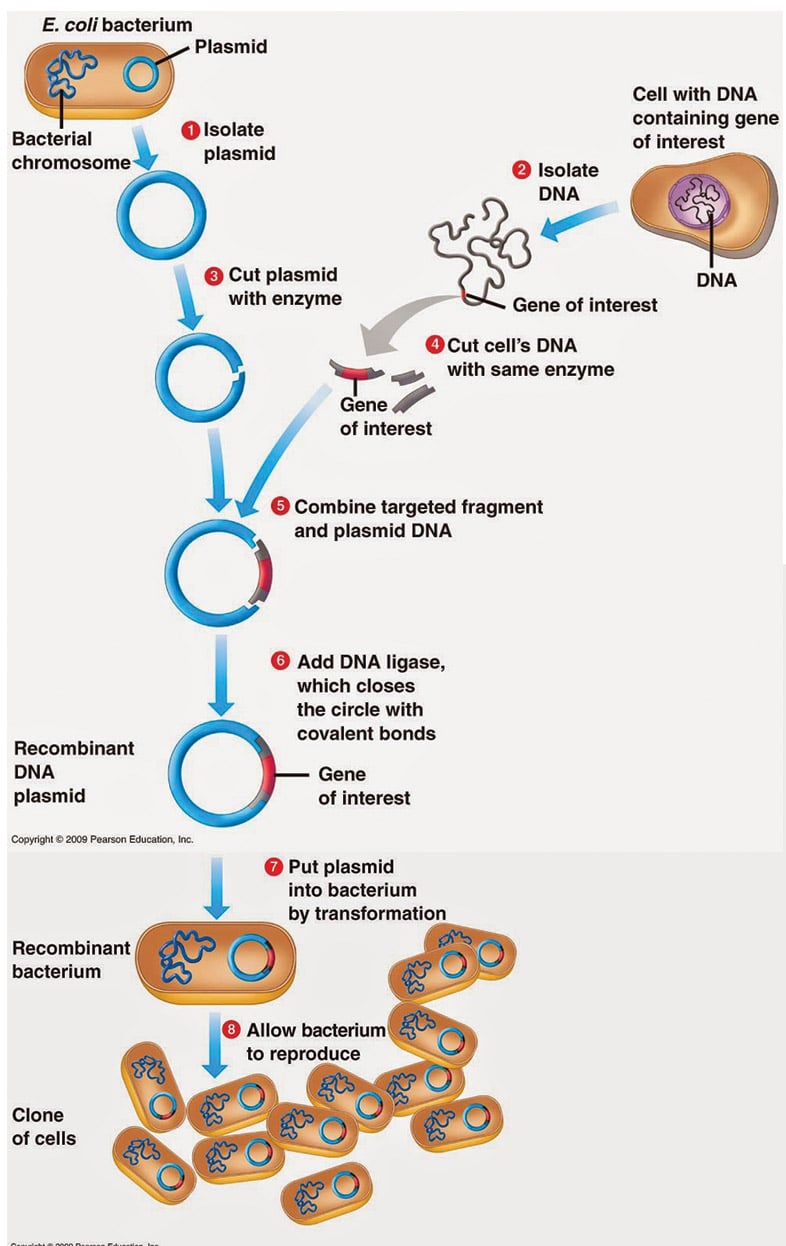
This protocol describes the basic steps involved in conventional plasmid-based cloning. DNA cloning is used in several applications. DNA Cloning takes place in the following steps.
Insert the plasmid into bacteria. Various techniques were introduced for assembling new DNA sequences 13 yet the use of restriction endonuclease enzymes is the most widely used technique in molecular cloning. This is known as a recombinant plasmid.
Plasmid vectors are available from both bacteria and. Long considered the traditional cloning method restriction ligation cloning permits the insertion of a DNA fragment of interest into a vector through a cut and paste procedure. Somatic cells on the other hand already contain two full sets of chromosomes.
The approach to producing an artificially cloned individual is to take the egg cell of one individual and to remove the haploid nucleus. The basic gene cloning steps are. To make a clone scientists transfer the DNA from an animals somatic cell into an egg cell that has had its nucleus and DNA removed.
1 Choice of host organism and cloning vector 2 Preparation of vector DNA 3 Preparation of DNA to be cloned 4 Creation of recombinant DNA 5 Introduction of recombinant DNA into host organism 6 Selection of organisms containing recombinant DNA 7 Screeni. The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. Cutting and Pasting DNA.
A plasmid also called a vector in this context is a small circular DNA molecule that replicates independently of the. The basic steps are. Slide 2 of 27.
The two methods used for reproductive cloning thus far are as follows. Then a diploid nucleus from a body cell of a second individual the donor is put into the egg cell. The egg is then stimulated to.
Cut open the plasmid and paste in the gene. Cloning Fact Sheet. The copied material which has the same genetic makeup as the original is referred to as a clone.
Cloning allows for the creation of multiple copies of genes expression of genes and study of specific genes. This protocol describes the basic steps involved in conventional plasmid-based cloning. The optimal vector and its host organism are then chosen based they type of insert and what will ultimately be done with it.
Cutting and Pasting DNA. A fragment of DNA containing a gene of interest is isolated inserted into the plasmid and transformed using a suitable bacterial host. However if restriction sites are incompatible or if.
The target gene is inserted into the cut site and is ligated by DNA ligase. The piece of DNA is pasted into a vector and the ends of the DNA are joined with the vector DNA by ligation. The egg develops into an embryo that contains the same genes as the cell donor.
A restriction enzyme that recognises a specific target sequence of DNA cuts it into two pieces at or near. Two types of enzymes are used in this method. Gene cloning is a simple yet complicated and highly sophisticated technique.
The Gene of interest is isolated at the end of the experiment using the antibiotic resistance gene. Coli recover the plasmid DNA and check for correct insertion events. The four main steps in DNA cloning are.
Steps and procedure. The chosen piece of DNA is cut from the source organism using restriction enzymes. For example lets see how DNA cloning is utilised to synthesise a protein such as human insulin in bacteria.
The green fluorescent protein GFP commonly used as an expression marker in molecular techniques was originally isolated from jellyfishIn cloning a gene it is helpful to use a cloning vector typically a plasmid or virus capable of independent replication that will stably carry the target DNA from one location to another. This process relies on restriction enzymes which cut DNA and DNA ligase which joins DNA. The goals are to insert a DNA fragment of interest into a receiving vector plasmid transform the plasmid into E.
As an example lets see how DNA cloning can be used to synthesize a protein such as human insulin in bacteria. Cloning the process of generating a genetically identical copy of a cell or an organism. Prokaryotic organisms organisms lacking a cell nucleus such as bacteria create genetically identical duplicates of themselves using binary fission or budding.
To get the DNA fragment into a bacterial cell in a form that will be copied or expressed the fragment is first inserted into a plasmid. This procedure starts with the removal of the chromosomes from an egg to create an enucleated egg. This inexpensive flexible method can be broken down into a basic two-step process.

Gene Cloning Steps Involved In Gene Cloning Online Biology Notes

Dna Cloning Process Steps Examples What Is Dna Cloning Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
No comments for "Describe the Basic Steps That Are Used in Molecular Cloning"
Post a Comment